Financial Management Bond valuation
재무관리-채권평가
7-(3)
1. Treasury Quotes
Bond Quotes
매수가격(Bid)과 매도가격(Ask)

Bid price: 사려는 가격
Ask price: 팔려는 가격
따라서 항상
Ask price >> bid price
Bid-ask price
=매수가격(Bid)과 매도가격(Ask)의 차이
= 수익

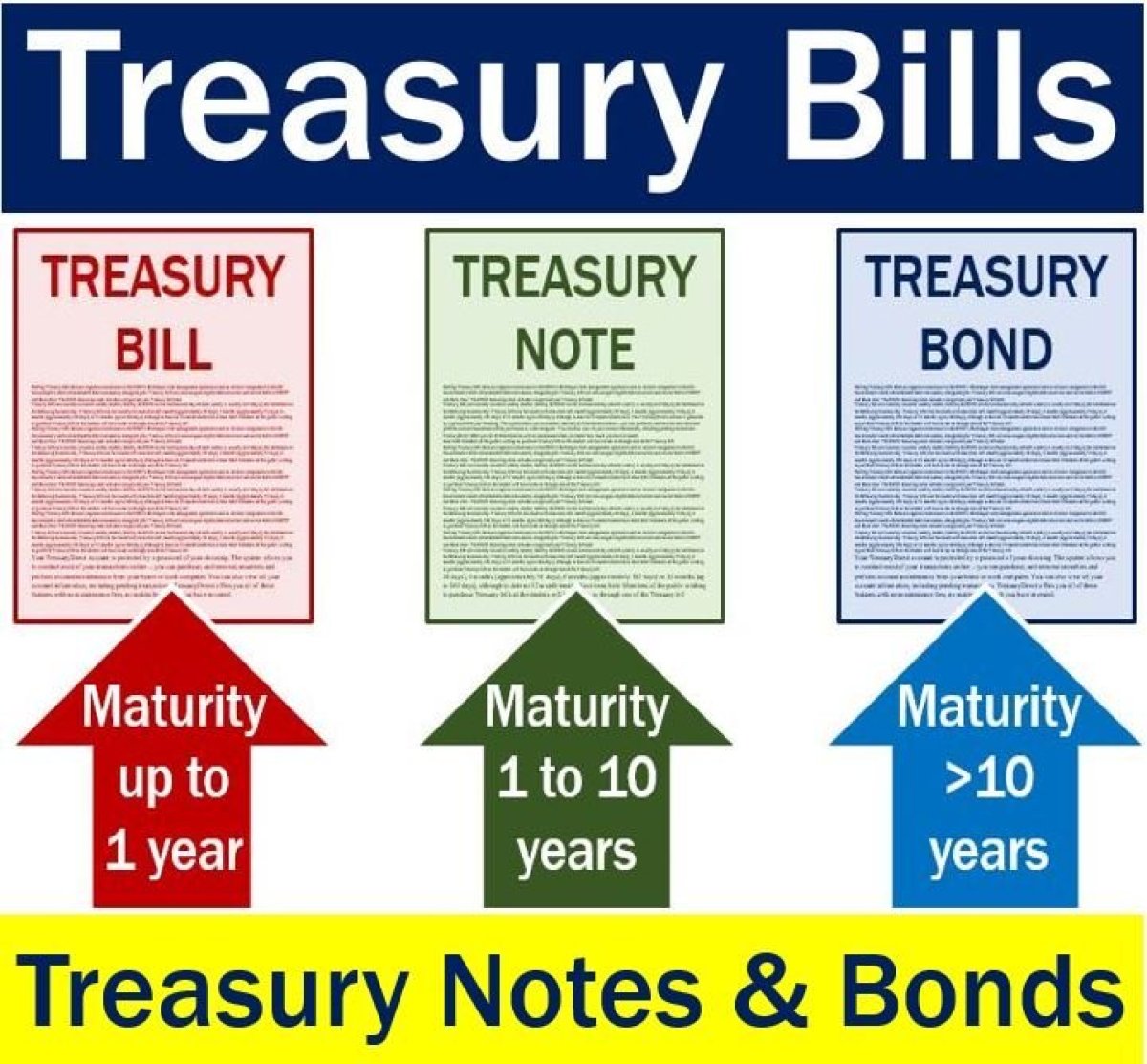
Treasury Bills :만기 1년이하 채권
Treasury Notes :만기 10년이하 채권
Treasury Bonds :만기 10년 초과 채권
2. Accrued interest.
금융에서 발생 된이자는 원금 투자 이후 축적 된 채권 또는 대출에 대한이자
또는 이전에 쿠폰 지급이 있었는지에 대한이자

Invoice price= quoted price + accrused interest
ex) Bond of 1,000 @12% payable semi-annually
Quote=1,060
Two months since last coupon payment of $60
= there are four months to the next semiannnual coupon date
3. Zero- coupon bonds
제로쿠폰채권(Zero Coupon Bond)은
쿠폰금리 없이 발행가격을 이자에 의해 할인·발행하는 채권을 말한다.
상환기간까지 이자 지급이 없는 것이 특징으로
one-time payoff of the pricipal at maturity

제로쿠폰채권(Zero Coupon Bond)은
coupon이 없기 때문에 PMT는 필요없고
오직 FV, PV, I/Y 만 필요함-> chapter 5의 식이랑 똑같음
4. real vs nominal rate
real rate
인플레이션 영향 고려 O
구매력 & 투자자 자본
nominal rate
인플레이션 영향 고려 X
일반적으로 YTM 등등은 nominal rate를 기반함
inflation rate가 주어지면
nominal rate-> real rate 구할 수 있음
when real rates of interest are high,
all other rates tend to be high
<fisher effect>

(1+R)=(1+r)(1+h)
R= nominal rate : 명목 이자율
r= real rate: 실질 이자율
h= expected inflation rate : 인플레이션율
ex) If we require a 10% real return
and we expect inflation to be 8%,
what is the nominal rate?
*R=(1+r)(1+h)-1
(1+0.1) X (1+0.o8)-1=0.188=>18.8%
*대략값= r+h => 실질이자율 + 인플레이션율
10% + 8% =>18%
*Doing PV calculations with inflation
If you are using nominal dollars in cash flow-> nominal rate of return
If you are using real dollars in cash flow-> real rate of return
don't mix them up!
5. what determines the YTM
YTM= market discount rate
만기수익률(YTM; yield to maturity)
using to calcualte the future cash flow
maturity of a bond (long, short)
확실성 낮음, 높음
The yields fo trasury bills and bonds reflect term structure of interest rate.
<what determines the YTM?>

1) Time value of money,r =>oportunity cost
(basic structure of YTM)
2) expected inflation, h =>inflation premium
3) Interest rate risk premium

<other determinants of yields>
default risks premium: 파산위험 증가하면 YTM 증가
Taxability premium(discount):할인위험 증가하면 YTM 증가
Liquidity premium:유동성 증가하면 YTM 감소
나에게 안전한 채권이면 YTM 만기수익률은 감소
나에게 위험한 채권이면 YTM 만기수익률은 증가
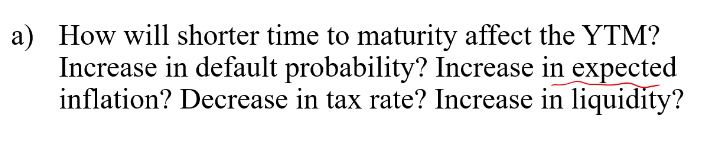

YTM 과 price는 반비례!
만기수익률과 가격은 반비례!!

따라서
shorter maturity-> 굿 YTM 감소 -> bond price 증가
increase in default probability->배드 YTM 증가
increse in expected inflation ->배드 YTM 증가
decrease in tax rate ->굿 YTM 감소
increase in liquidity -> 굿 YTM 감소
'정보' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 코로나19 , 넷플릭스 그리고 OTT산업 (0) | 2020.05.20 |
|---|---|
| Financial Management -stock valuation (0) | 2020.05.20 |
| Financial Management -Bond valuation 채권평가 (0) | 2020.05.18 |
| [2020 인기 있는 여자 영어 이름] (0) | 2020.03.20 |
| [코로나/넷플릭스] 코로나 바이러스와 넷플릭스의 상관관계 (0) | 2020.03.20 |




댓글